What is FDM 3D printing?
Let's start with the fact that this is one of the most common and simplest 3D printing technologies. FDM 3D printers are the most budget-friendly and accessible in every way. What's more, some craftspeople assemble these devices themselves. In a way, this kind of “handmade” FDM 3D printing is pretty successful, but it's nothing like printing with specialized equipment.
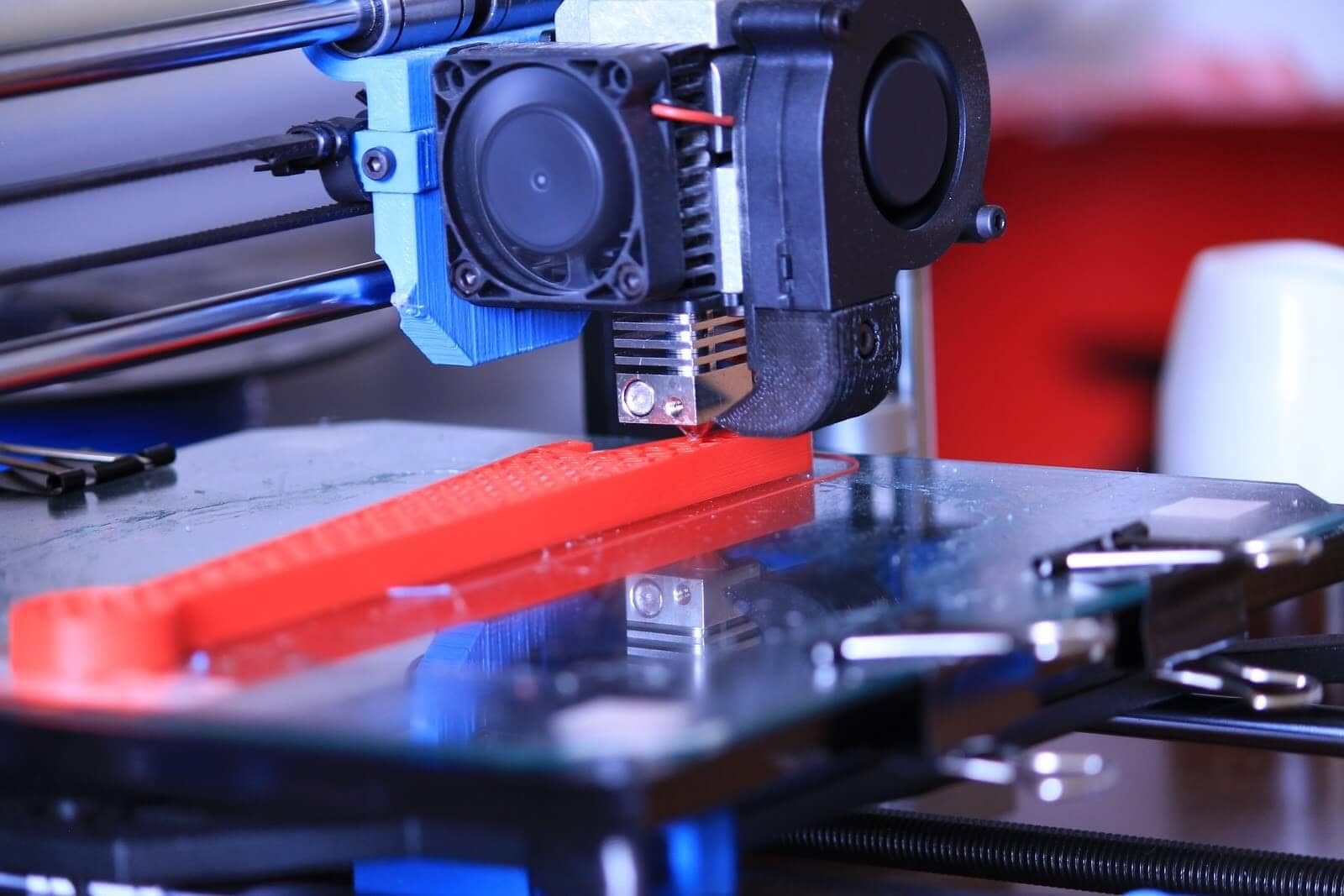

So, what is FDM 3D printing? FDM is an abbreviation for “Fused Deposition Modeling.” This description pretty much sums up FDM 3D printing. But for a first encounter and introduction to the technique, that's not enough, so we'll tell you all about this technology in detail.
How FDM 3D printing works
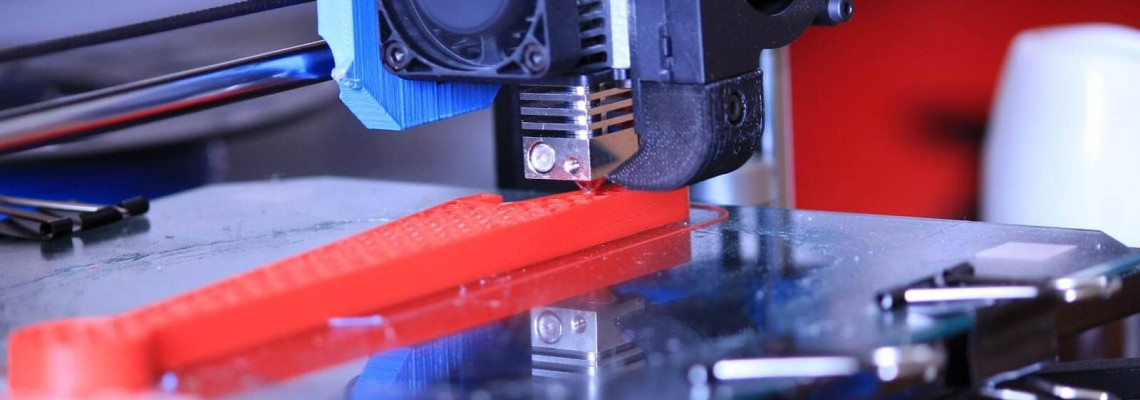
As with any other additive manufacturing technique, the essence of FDM 3D printing lies in the layer-by-layer reproduction of three-dimensional objects based on digital data (3D models). Special plastic filaments are used as the material in FDM 3D printers for this purpose. These filaments can have a diameter of 1.75 mm or 2.85 (3) mm.
Essentially, FDM 3D printing is the continuous feeding of material filament into an extruder (print head) equipped with a heating element. The latter is designed to heat the nozzle through which the material is fed. At this stage, the plastic is melted and extruded (pressed) onto the 3D printer platform. Each subsequent layer is extruded onto the previous one along a predetermined trajectory, which is how the product is constructed. For a smoother feed of material and faster hardening of layers, extruders are equipped with external fans that create a sharp temperature drop.
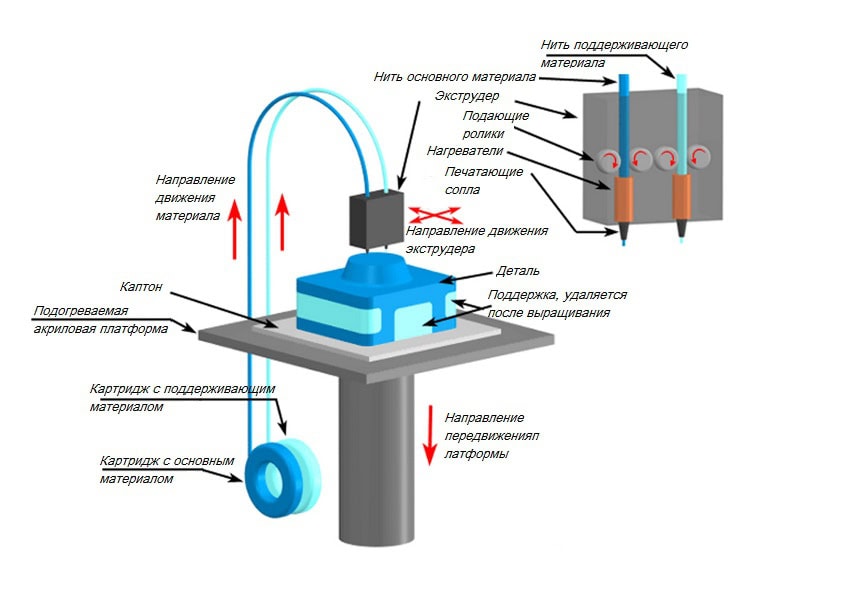
Some FDM 3D printers are equipped with a heated platform, which allows them to work with more “capricious” materials, such as ABS plastic. Often, such printers also come with a closed housing. There are also devices with double and even triple extruders, which allow you to work with several types of 3D plastic at the same time. As a rule, in such cases, one material is the main one, and the second is auxiliary. Often, a water-soluble support material (PVA plastic) is chosen as the auxiliary material.
Stages of FDM 3D printing
For convenience, we have divided the process of manufacturing objects into sequential stages:
- Development of a 3D model in special programs (Autodesk 3DsMAX, ZBrush, Maya, Blender, SolidWorks, etc.);
- Checking the finished model for suitability for 3D printing, for example, in NetFabb (the 3D model should not contain holes, broken edges, inverted polygons, etc.). More details about model preparation can be found in this article;
- Loading the 3D model into the slicer program. At this stage, the necessary 3D printing settings (speed, temperature, etc.) are selected, and support structures are generated if there are overhanging elements in the model. Upon completion of the preparatory part, the program generates control code (G-code) for the 3D printer based on digital data (models) and selected settings;
- Transfer of the control code to the 3D printer. A USB flash drive or SD card with the recorded G-code (in advanced 3D printer models, it is also possible to transfer the file via a Wi-Fi wireless network) is connected to the device, in the menu of which the necessary file is selected and printing is started.
- Upon completion of 3D printing, the finished product is detached from the 3D printer table, cleaned of supports and excess plastic.
Materials used
FDM 3D printing boasts a wide variety of available materials. A huge amount of plastic is available for use with FDM 3D printers, but not every printer supports the entire range of materials offered on the market. This factor depends on the melting point of a particular material and the maximum heating temperature of the device's nozzle. Roughly speaking, devices whose nozzle does not heat up to more than 250 °C will not be able to print with materials with a melting point of 280 °C.
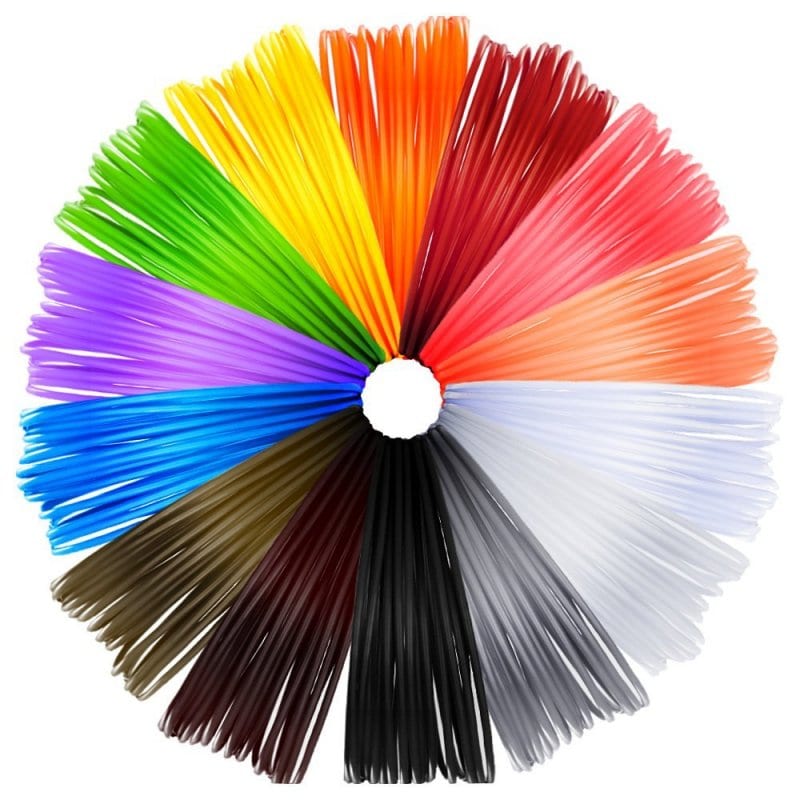

If we disregard this limitation, then in terms of the choice of consumables, FDM 3D printing can safely be called the most versatile additive manufacturing technology. Users can work with plastics of all colors and shades, transparent, glossy, and matte polymers, flexible and rigid engineering materials, metallized plastics, and color-changing plastics. Water-soluble, fluorescent, luminescent materials, wood-filled plastic, and much more are also available.
Advantages of FDM technology
As you already understand, FDM 3D printing is of great interest to both private users and commercial organizations. Let's summarize its advantages:
- Affordability. This type of 3D printing is the most affordable in financial terms, which explains the high popularity of FDM 3D printers;
- Wide range of materials. As you already know, it is not very difficult to find materials for FDM 3D printing. Moreover, such 3D plastic is also quite affordable.
- Functionality. Not only because of the huge selection of consumables, but also because of the characteristics of the FDM method itself, 3D printers can be used for a wide variety of tasks, which makes them extremely popular;
- Price/quality ratio. Modern FDM 3D printing devices boast excellent object reproduction quality (up to 40 microns!) at a relatively low cost. Add to this the other advantages, and you will understand the reason for their success!
Areas of application for FDM 3D printing
Due to its versatility, FDM 3D printing can be used for virtually any purpose. And thanks to the possibility of post-processing (painting, sanding, varnishing) of finished products, its areas of application are expanding even further.
Let's take a closer look at them:
- Prototyping;
- Manufacturing of functional components;
- Small-batch production;
- Modeling;
- Creation of medical models;
- Design;
- Architectural modeling;
- Souvenir products;
- Cosplay;
- Car tuning.
Types of FDM 3D printers
3D printers for modeling using layer-by-layer deposition are divided into two types based on the type of coordinate system:
- With a rectangular coordinate system (XYZ axes);
- With a cylindrical coordinate system, or delta printers.
Our store offers a wide range of devices of both classes with various characteristics, including:
- KLEMA 3D printers;
- CreatBot 3D printers in assortment;
- Leapfrog 3D printers;
- Raise 3D printers and many others.
This concludes our article. Thank you for reading, and be sure to check out other articles in the section on types of 3D printing. For more information on the availability of 3D printers and FDM printing capabilities, please call or email us using the contact details provided in the “Contacts” section. Get in touch, we look forward to working with you!























































Leave a Comment