3D биопечать
Область 3D биопечати ежедневно преображается и совершенствуется. Благодаря усилиям исследователей со всего мира на сегодняшний день 3D биопечать развивается наиболее стремительно и является чрезвычайно перспективной отраслью трёхмерных технологий. Несмотря на то, что большинство передовых разработок пока находятся на стадии тестирования, новые улучшенные схемы массово выходят в свет, составляя конкуренцию существующим методикам 3D биопринтинга. Принцип технологий всегда один, но светлые умы человечества находят инновационные способы обыграть имеющиеся приёмы 3D биопечати.
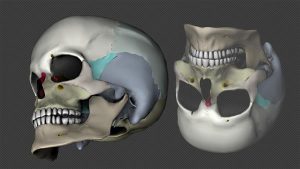
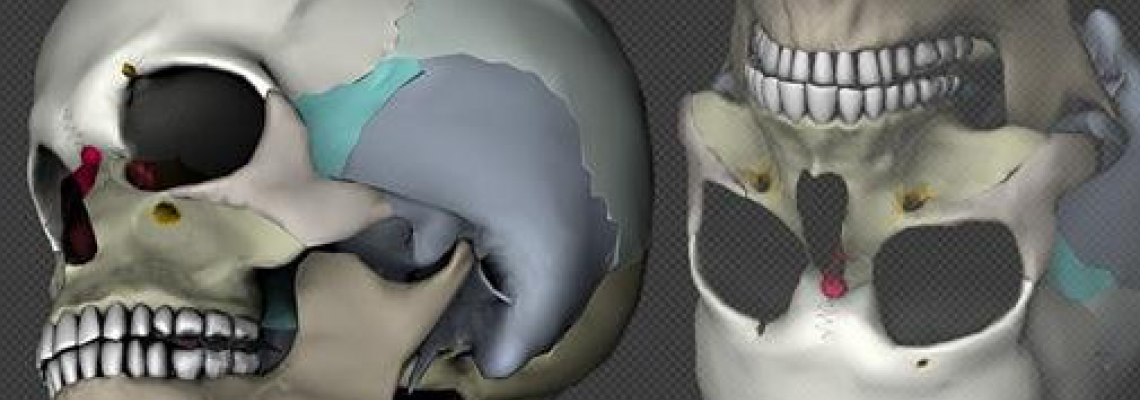
Так, группа исследователей из Ирландии разработала новую технику: 3D биопечать крупных и сложных структур хрящевых имплантатов. Подобные конструкции являются оптимальной основой для восстановления костных тканей, к чему стремится множество специалистов в сфере биопечати. Команда учёных из научно-исследовательской организации Amber в городе Дублин, Ирландия, намеревается применить 3D биопечать в изготовлении различных имплантатов нового поколения. Данный центр специализируется на исследовании разнообразных материалов для 3D печати, и поле его деятельности не ограничивается медицинской сферой. Исследователи работают также в области наноэлектроники и занимаются печатью инновационных аккумуляторов на 3D принтере.
Кости на 3D принтере
По мнению учёных, их разработка может найти широкое применение в спинальной хирургии, а также в лечении пациентов с черепно-мозговыми проблемами. Причём в специфике болезней нет никаких ограничений — это могут быть как приобретённые, так и врожденные заболевания, травмы и повреждения. Можно печатать абсолютно любые кости на 3D принтере. Вкратце, 3D биопечать костных имплантатов заключается в создании так называемого «шаблона» для имплантата из органических биоматериалов и стволовых клеток. Готовая структура может быть сразу вживлена пациенту, после чего начнётся процесс формирования кровеносных сосудов и твёрдой костной ткани. Преимуществом технологии является отсутствие необходимости долгого «выращивания» живых тканей в лабораторных условиях.

Готовый шаблон может быть сразу имплантирован непосредственно в место повреждения, где со временем он превратится в полностью функционирующую часть человеческого организма. Такая 3D биопечать представляет собой достойную альтернативу не только современным титановым имплантатам, но и процессам алло- и аутотрансплантации. Несмотря на широкое применение в медицине, каждая из последних сопряжена с рядом трудностей, преодолеть которые бывает нелегко. К примеру, при аллотрансплантации наиболее распространёнными проблемами является отторжение вживляемых тканей и передача с ними различных заболеваний. 3D биопечать костных трансплантатов таких опасностей в себе не несет.
Преимущества 3D биопечати
Аутотрансплантация неприятна своей болезненностью, вдобавок к чему её нередко сопровождают различного рода послеоперационные осложнения. Неудивительно, что в сложившейся ситуации учёные возлагают большие надежды на технологию 3D биопечати. По последним исследованиям в этой сфере очевидно, что она предоставляет возможность производить восстановление костных тканей без сравнительных затруднений из собственных клеток пациента. Преимущества 3D биопечати исключают неприятные последствия, типичные при аллотрансплантации. Что касается технологии Amber, её разработчики планируют для начала использовать методику в изготовлении имплантатов коленных и тазобедренных суставов.
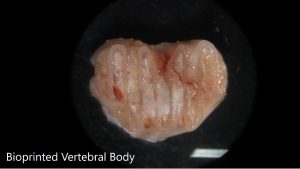
Команда уже провела успешное тестирование первых 3D-печатных структур, во время которого шаблоны сегмента позвоночника был вживлены под кожу пациента. Спустя время имплантат покрылся полностью функционирующей костной тканью с кровеносными сосудами, что доказывает эффективность проекта. Следующей целью учёных является применение методики в лечении крупных дефектов костей, с дальнейшей оптимизацией процесса настолько, что с его помощью станет реальным восстановление коленного сустава целиком. Исследователи уверенны, что у проекта есть все шансы выйти за рамки существующих возможностей 3D биопечати. В самом деле, методика позиционирует себя в качестве одного из наиболее интересных достижений в данной сфере. Удивительно наблюдать за тем, как технология, изначально нацеленная на быстрое прототипирование, постепенно меняет не только сферу медицины, но и мир в целом.






































Оставить комментарий