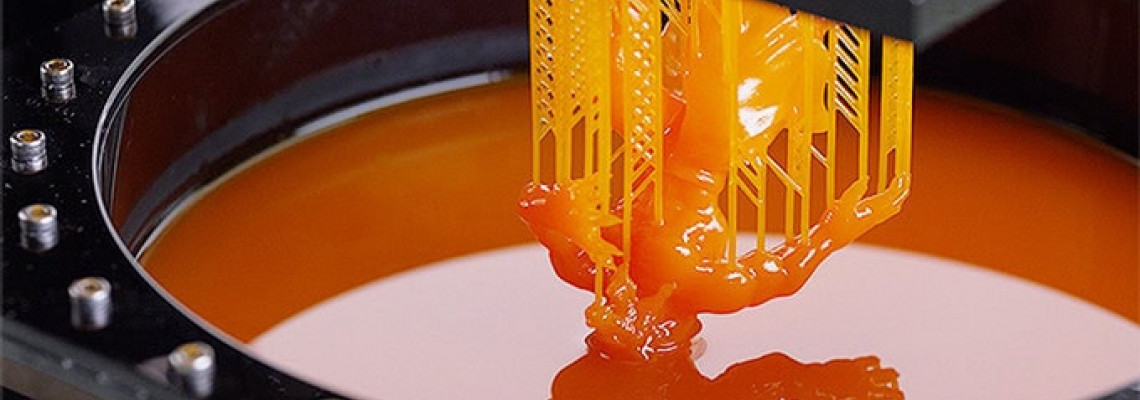
Що таке 3D друк SLA?
Лазерна стереолітографія, вона ж 3D друк SLA, є не тільки однією з перших 3D технологій у світі, але й однією з найточніших методик адитивного виробництва. В деякому роді вона унікальна, адже в ній в якості витратного матеріалу застосовується рідка фотополімерна смола. Суть технології полягає в засвіченні фотополімеру за певним алгоритмом (заданим програмою-слайсером на основі 3D моделі). Під впливом лазерного випромінювання смола застигає, формуючи готовий об'єкт.
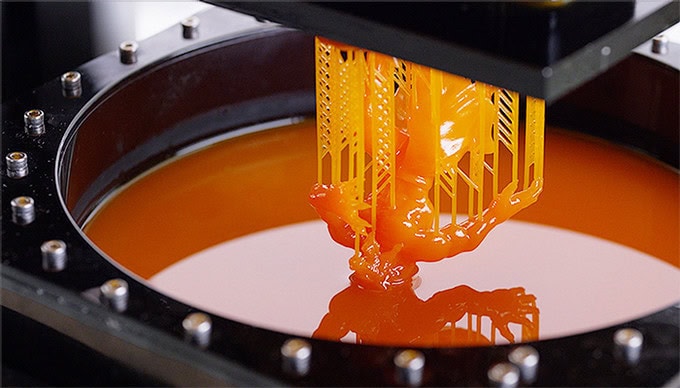
Як і в FDM 3D друку, 3D друк SLA паралельно з побудовою об'єкта вимагає побудови опорних структур при наявності в моделі нависаючих елементів. По суті, ця методика нагадує SLS 3D друк, але замість порошку виступає рідкий фотополімер. В іншому це те ж саме пошарове відтворення виробів за заданими 3D моделями. Більш докладно про те, як функціонує 3D друк SLA, ми розповімо нижче.
Особливості роботи
Для того, щоб зрозуміти, як відбувається процес 3Д друку, необхідно розібратися з тим, як влаштований SLA 3D принтер. У цьому вам допоможе зображення, прикріплене нижче, на якому зображена схема класичного стереолітографічного принтера. Ми говоримо класичного, тому що саме такою є запатентована технологія SLA друку. Така конструкція також застосовується в промислових пристроях для 3D друку SLA. Що стосується вже введених в ужиток настільних SLA 3D принтерів, в них використовується так званий «3D друк SLA догори ногами». Що це означає?
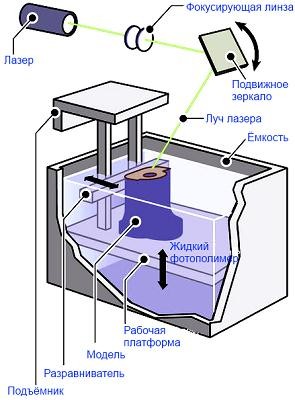
Спочатку опишемо процес друку на зображенні вище. У ньому лазер розташований зверху, а робоча платформа поступово опускається вниз. Отже, в ємність з фотополімером занурюється сітчаста платформа, на глибину не більше 0,05-0,13 мм (саме такою є товщина шару). Після чого активується лазер, який впливає на певні ділянки матеріалу (задані програмою). Вплив лазерного випромінювання викликає затвердіння першого шару фотополімеру. Далі платформа опускається ще на шар нижче, лазер знову активується, продовжуючи формувати об'єкт, і так до остаточного побудови виробу.
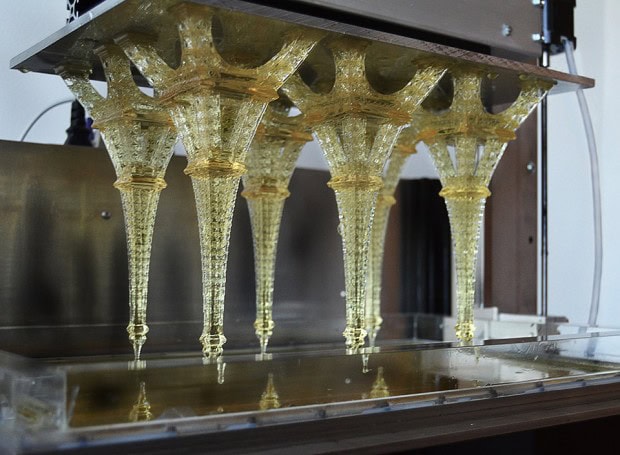

Що стосується процесу 3D друку, що застосовується в настільних 3D принтерах, принцип абсолютно той же. З тією лише різницею, що лазер розташований під ємністю з фотополімером, а при побудові виробу платформа не опускається, а поступово піднімається вгору. Спільним для обох варіантів є промивання виробу в спеціальних розчинах після завершення 3D друку, а також опромінення готової моделі ультрафіолетовим світлом. Перше потрібно для остаточного очищення виробу від залишків фотополімеру, а друге для повного затвердіння виробу.
Відмінності від DLP 3D друку
На основі SLA 3D друку розроблено кілька інших методик, однією з яких є DLP 3D друк. З огляду на набуття останньої достатньої популярності, ми вважали за доцільне сказати кілька слів і про неї. Принципової різниці між цими методиками немає, але про деякі відмінності слід згадати. Отже, чим же 3D друк SLA відрізняється від DLP 3D друку? Все дуже просто: замість лазера в DLP 3Д принтерах використовується проектор, який засвічує цілий шар одночасно, а не поступово, як лазер в стереолітографії.
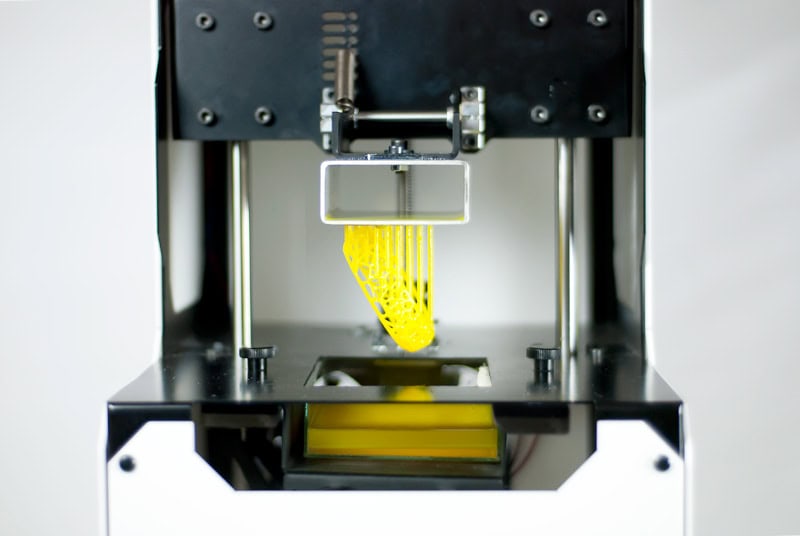
Вважається, що за рахунок цього DLP друк дозволяє відтворювати об'єкти трохи швидше. Однак ця різниця не настільки велика, щоб витіснити стереолітографічні принтери з ринку 3D друку. Крім того, в 3D-принтерах DLP застосовуються фотополімерні смоли з іншою довжиною хвилі засвічення, а якість 3Д-друку на деяких моделях поступається якості друку SLA-принтерів. Але, повторимося, істотних відмінностей між технологіями немає.
Застосовувані матеріали
Як ми писали вище, в 3D принтерах, що працюють за технологією лазерної стереолітографії, застосовуються рідкі фотополімерні смоли, які ще називають фотополімерами. Це особливі речовини, які змінюють свої властивості під впливом світла. Найчастіше активним випромінюванням є ультрафіолетове. Стоматологам добре знайомий термін «фотополімер», адже аналогічні речовини широко застосовуються в стоматологічній практиці. По суті, це той випадок, коли одна річ має кілька різних застосувань.
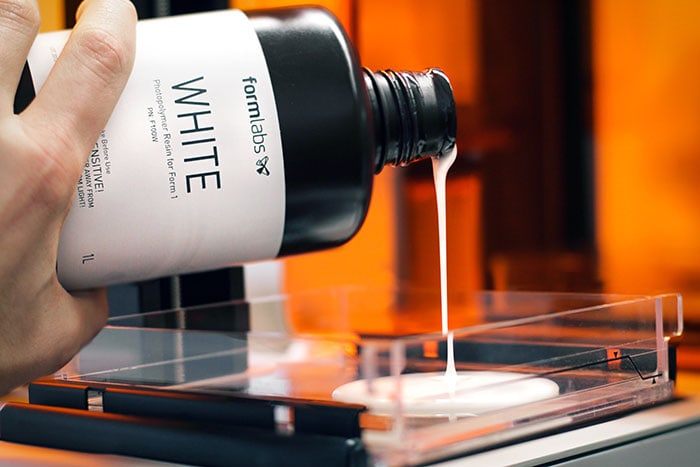

Які ж фотополімери використовує 3D друк SLA? Найрізноманітніші. Навіть на ринку настільних 3D принтерів сьогодні можна знайти гнучкі і жорсткі, інженерні і декоративні, стоматологічні і випалювані фотополімерні смоли всіх кольорів і відтінків. Звичайно, асортимент ще не настільки широкий, як, наприклад, у FDM 3D друку, але саме 3D друк SLA і витратні матеріали до нього знаходяться на другому місці за популярністю серед користувачів.
3D друк SLA: переваги та сфери застосування
Почнемо з переваг, які надає користувачам 3D друк SLA. Торкнемося як промислових, так і настільних пристроїв для відтворення об'єктів. Отже, ось плюси методики:
- 3D друк високої точності;
- Виготовлення виробів будь-якої складності;
- Великий вибір різних матеріалів;
- Можливість виготовлення готових до використання виробів;
- Низька витрата матеріалу на підтримувальні структури.
Тепер опишемо сфери застосування методики:
- Ювелірна справа;
- Стоматологія;
- Дизайн;
- Макетування;
- Прототипування;
- Виготовлення моделей для лиття під тиском.
І в цілому все, де потрібне відтворення 3D моделей у високій якості, адже саме 3D друк SLA дозволяє отримувати надзвичайно деталізовані вироби навіть крихітних розмірів. А завдяки наявності на ринку випалюваних фотополімерів можливість лиття за надрукованими моделями значно спрощується.
Обладнання
Щоб краще ознайомитися з 3Д принтерами, що застосовуються в цій технології друку, загляньте в наш розділ «SLA 3D принтери», де розміщені різноманітні пропозиції щодо обладнання даної категорії. Зокрема, у нас представлені такі прилади:
- Form 4 від Formlabs;
- 3D-принтери KLD в асортименті;
- SLA 3D принтери Wanhao;
- 3Д принтери LiquidCrystal;
- B9Creator і багато інших.
За детальною інформацією про це та інше обладнання звертайтеся за телефонами або електронною поштою, вказаними в розділі «Контакти». Будемо раді співпраці!











































Залишити коментар